https://doi.org/10.1121/1.5100911
Abstract:
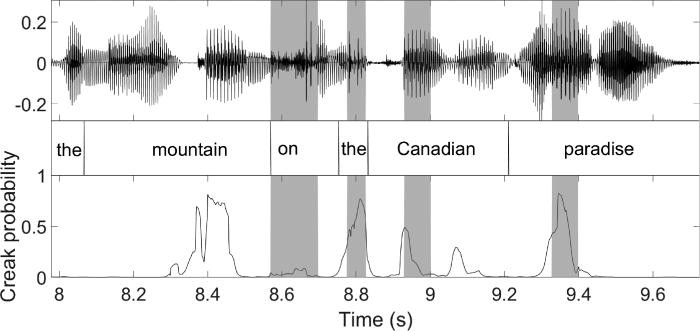
Irregular pitch periods (IPPs) are associated with grammatically, pragmatically, and clinically significant types of nonmodal phonation, but are challenging to identify. Automatic detection of IPPs is desirable because accurately hand-identifying IPPs is time-consuming and requires training. The authors evaluated an algorithm developed for creaky voice analysis to automatically identify IPPs in recordings of American English conversational speech. To determine a perceptually relevant threshold probability, frame-by-frame creak probabilities were compared to hand labels, yielding a threshold of approximately 0.02. These results indicate a generally good agreement between hand-labeled IPPs and automatic detection, calling for future work investigating effects of linguistic and prosodic context.
