Pritpal S. Kanhaiya, Andrew Yu, Richard Netzer, William Kemp, Derek Doyle, Max M. Shulaker
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c04194
Abstract:
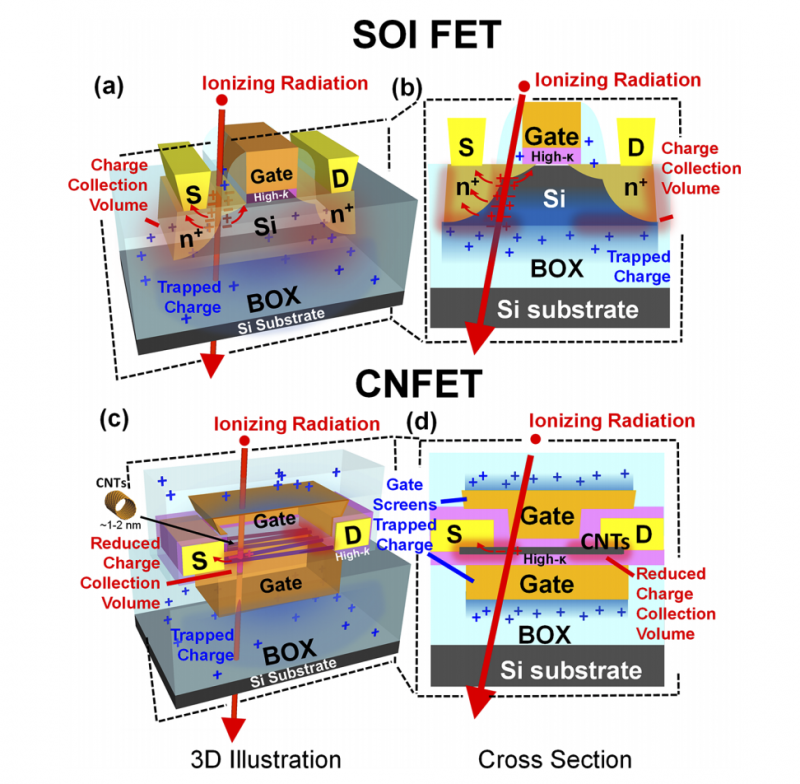
Electronics for space applications have stringent requirements on both performance and radiation tolerance. The constant exposure to cosmic radiation damages and eventually destroys electronics, limiting the lifespan of all space-bound missions. Thus, as space missions grow increasingly ambitious in distance away from Earth, and therefore time in space, the electronics driving them must likewise grow increasingly radiation-tolerant. In this work, we show how carbon nanotube (CNT) field-effect transistors (CNFETs), a leading candidate for energy-efficient electronics, can be strategically engineered to simultaneously realize a robust radiation-tolerant technology. We demonstrate radiation-tolerant CNFETs by leveraging both extrinsic CNFET benefits owing to CNFET device geometries enabled by their low-temperature fabrication, as well as intrinsic CNFET benefits owing to CNTs’ inherent material properties. By performing a comprehensive study and optimization of CNFET device geometries, we demonstrate record CNFET total ionizing dose (TID) tolerance (above 10 Mrad(Si)) and show transient upset testing on complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) CNFET-based 6T SRAM memories via X‑ray prompt dose testing (threshold dose rate = 1.3 × 1010 rad(Si)/s). Taken together, this work demonstrates CNFETs’ potential as a technology for next-generation space applications.
